Hygiene • Water Conservation • Performance • Compliance
The plumbing requirements for restroom fixtures in commercial and institutional facilities have evolved from conventional lever and knob-operated plumbing to complete plumbing systems controlled by sensors. The touch faucet has emerged as the cornerstone of efforts to optimize hygiene, conserve water, and meet plumbing requirements in high-density applications such as airports, hospitals, collegiate institutions, and government organizations. When evaluating rest room fixtures, design professionals must consider longevity, sustainability, and performance on all counts.

The Need for Touchless Faucets in Contemporary Toilet Designs
Touchless faucets are also popularly known as automatic or sensor-controlled faucets. Such faucets make use of proximity or time-of-flight sensing. Such types of faucets are useful for turning on the flow of water only if it is needed. As per the standard conventions used in the industry, such types of faucets are the ones where presence sensing along with the control of valves happens in an automatic way. This, in turn, leads to minimized spread of germs as well as wastage. For more details, see the source links below.
Speaking from a building design and engineering perspective, touch technology is a much, much bigger concept with regard to building performance factors, aside from simply clean hands, including, for instance, health, sustainability, and efficiency.
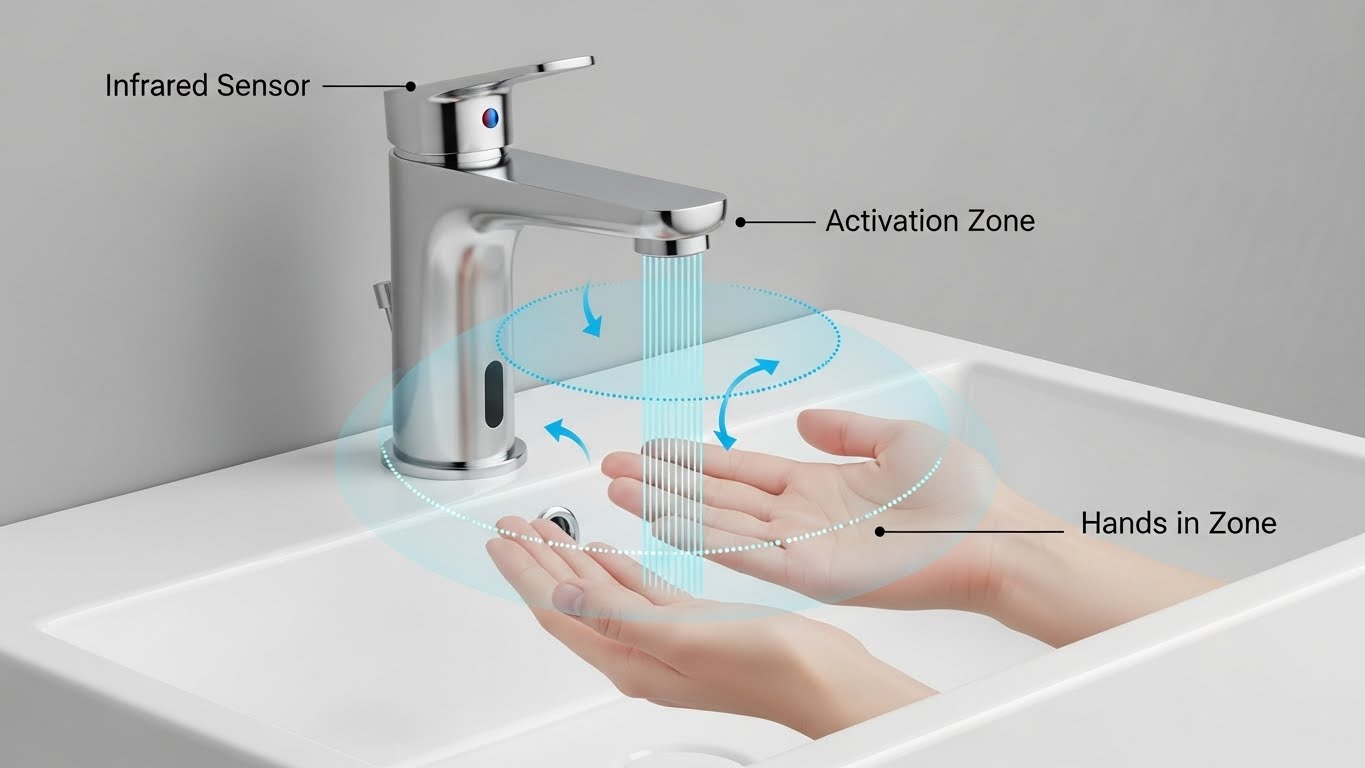
Engineering Principles That Underlie Touchless Technology
Sensor Technologies
Present day commercial sensor faucets incorporate several sensor technologies:
IR Proximity Sensors – These rely upon the variation in the IR rays to trigger the action of the valve opening. IR sensors tend to be disturbed by other light sources if not positioned well.
Time-of-Flight (ToF) Sensors – How ToF sensors work is by calculating how long it takes for the vicinity of near-infrared light emitted by the sensor to reflect back from the hand or object. These sensors work better when it comes to measuring distances within a bathroom setting regarding removing false activation from basin geometry and reflections. Information about this technology can be found in the source links below.
In relation to the engineering specification, the algorithms of the sensors have to focus more on adaptive calibration and signal processing, capable of damping the transient activation while also ensuring the registration of the intended use.
Hydraulic and Solenoid Valves Design
Touchless faucets use a solenoid valve, which is controlled by the microcontroller unit, or MCU, for the regulation of the water flow. The requirement for the solenoid valve is that it should provide an absolute mechanical seal, withstand millions of cycles, and completely match the pressure-compensating flow regulators. This is necessary for the application of the specified flow rates, which are required by the standards ASME A112.18.1/CSA B125.1. The performance of the water usage and the pressure of the supply, for instance, the pressure of 20-80 psi, should be demonstrated by standardized tests required by the standards of the plumbing. For more details, see the source links below.
Coordination of Power and Electronics
In commercial toilet designs, there are three types of power methods:
Battery Powered: It enables easy deployment and availability but comes with maintenance planning to address the battery life and accessibility factor.
Low Voltage DC or Hardwired:
It provides a strong power supply, making it simple to integrate it with the Building Automation System.
Energy Harvesting: Research and Development activity focused on exploring the latest advancements for harvesting energy from or kinetic energy of water to minimize reliance on batteries and thus eliminate any wastage.
Electronic circuits must be made resilient against electromagnetic interference (EMI) as well as surge protection in order to operate efficiently in an electrical environment.
Accordance with Regulatory Requirements and Performance
ADA Accessibility
Americans With Disabilities Act Accessibility Guidelines: One critical component under the Americans With Disabilities Act Accessibility Guidelines is accessible reach ranges, floor space, or the accessible parts requiring actions by the individual that do not involve tight gripping, pinching, or turning of the body or limbs. All touchless faucets are inherently accessible under the Americans With Disabilities Act Accessibility Guidelines because they do not require the use of faucets or handles. The designer, however, must check if the sensor control area provides accessible reach ranges under the Americans With Disabilities Act Accessibility Guidelines. This is particularly important for persons with limited mobility to control the faucets. For more details on accessibility, see the source links below.
WaterSense and Water Efficiency
WaterSense sets the guidelines for the use of water in order for designers to be able to rate the efficiency of faucets. WaterSense is more concerned with household products, yet guidelines in residential toilets (such as max rates of 1.5 gpm or gpm, respectively, on private lavatory fixtures) help the concerned reader understand information about commercial toilets specifically for WaterSense. Numerous local and state codes, such as CalGreen, set rates even further down at public facilities with rates for public lavatory faucet water set at or below 0.5 gpm. More information on WaterSense guidelines is found in the source links below.
CALGreen and Green Building Regulations
The CALGreen code in California (Title 24, Section 11) is the only water-efficient code in the country and is a model for the whole of America. To meet all requirements of CALGreen, the designers must take into consideration the rates for water fixtures. The state of California is one region where it is necessary to meet all requirements of state and/or city codes to certify a sustainable project.

ASME A112.18
ASME A112.18.1/CSA B125.1 provides performance procedures and tests applicable to plumbing supply fittings, including touchless faucets. Performance specifications, including duration, leakage, flow rate at standard pressure, and material, are available via this standard. Compliance with ASME standards ensures all plumbing supply fittings meet specified performance criteria acceptable to codes and consulting engineers. For more information about these standards, please see the source links below.
Touchless faucets in a business environment have to be able to handle millions of cycles in their lifetime. Factors that affect durability are:
Material used: Brass with higher durability and Resistant finishes are highly durable against normal wear and tear and environmental conditions for toilets. Solenoid mechanisms will need to use Seismic-rated or Heavy Duty cases to provide long-lasting durability for decades when used heavily. More details about the materials are given in the source links below.
Ingress Protection: Components must be rated high on ingress protection, for example, IP65 or higher. This will prevent damage from moisture, soap, or humidity present in restrooms. More on ingress protection can be found in the source links below.
Key Feature Importance Table
| Key Feature | Importance Rating (1-10) |
|---|---|
| Water Conservation | 9 |
| Water-efficient touchless faucets help minimize water waste, aligning with sustainability goals and water usage regulations. | |
| Durability | 8 |
| High-quality materials ensure the faucet system withstands heavy usage in commercial environments. | |
| ADA Accessibility | 7 |
| Ensuring that faucets meet ADA accessibility guidelines is crucial for compliance in public spaces. | |
| Sustainability | 9 |
| Eco-friendly materials and design concepts have also been incorporated. This enhance green building design. | |
| Performance Compliance | 8 |
| By meeting industry standards, one gets assured performance and a longer life span . These include ASME, CALGreen, and more. | |
| System Integration | 7 |
| The ability to connect touchless faucets with building management systems (BMS) for enhanced maintenance and efficiency. | |
| WaterSense Compliance | 8 |
| WaterSense certified faucets help in water conservation efforts and are efficient enough. | |
| Flow Rate Performance | 9 |
| Ensures faucets perform optimally in high-traffic commercial environments while conserving water. | |
| Serviceability | 7 |
| Easy Maintenance and Repair are must. They ensure long performance and economical operation. | |
| Energy Efficiency | 8 |
| Low energy usage and eco-friendly energy sources lower expenses. | |
| Material Durability | 9 |
| Using durable and noncorrosive material helps the faucet to last long even in a tough office environment. |
