Commercial restrooms are small mechanical rooms in plain sight. A touchless faucet in a corporate lobby or transit hub has to satisfy user experience, accessibility, water budgets, and maintenance reality while operating thousands of cycles per month. For AEC teams, the “right” faucet is rarely about appearance. It is about performance under variable supply conditions, serviceability, and predictable compliance paths.
This article reviews FontanaShowers’ commercial touchless faucet line through an engineering and specification lens, with emphasis on durability, sustainability, and system integration in institutional environments.

Relevant product and category references (FontanaShowers)
- Touchless Restroom
- Touchless Faucet
- Best Touchless Bathroom Faucet
Example product page
- Commercial Bathroom Matte Black Automatic Touchles
Performance Framework for Commercial Touchless Faucets
Define the duty cycle and failure modes
High traffic restrooms push three common failure modes: sensor drift or false triggering, fouling at strainers and aerators, and power related downtime. A practical performance framework starts with the expected uses per day, cleaning chemistry exposure, and whether the faucet must tolerate reflective surfaces, varying ambient light, and splashback.
When reviewing FontanaShowers commercial touchless listings, prioritize products that clearly document:
- Operating pressure range and recommended filtration or in line strainers
- Power method and replacement intervals
- Flow control method and rated flow or cycle volume
- Access to solenoid, electronics, and check components without removing the entire fixture
FontanaShowers category pages indicate availability of commercial electronic faucets with posted specification and installation documentation on product listings, which is a baseline expectation for spec grade selection and submittal workflows.
Touchless Restroom
Accessibility and Usability in Public and Corporate Restrooms
ADA alignment for controls and reach
Touchless activation can support accessibility goals by reducing grasping, pinching, and twisting. However, ADA compliance depends on the full installation, including spout reach, clearances, sink geometry, and mounting height. For most projects, teams reference the 2010 ADA Standards and then coordinate with the selected lavatory, mirror, and accessories.
2010 ADA Standards landing page:
- 2010 ADA Standards (Landing Page)
Combined ADA Standards PDF:
- ADA Standards (PDF)
Key coordination items for drawings and schedules:
- Sensor location and effective activation zone relative to bowl and user posture
- Spout outlet position relative to drain to reduce backsplash
- If the faucet includes temperature control, ensure the control location and operability remain accessible

User safety and temperature control strategy
In public restrooms, temperature control is typically handled by a central thermostatic mixing valve, a point of use mixing valve, or a controlled hot limit approach. Touchless faucets can be specified with cold only operation where permitted, but many corporate or hospitality environments prefer tempered water for usability. From a risk standpoint, scald mitigation is an MEP system decision that must align with owner policy, local plumbing code, and fixture capabilities.
Standards and Compliance Considerations for Submittals
ASME performance and plumbing supply fittings
For commercial lavatory faucets, ASME A112.18.1 and CSA B125.1 are widely used reference standards for plumbing supply fittings performance and testing expectations. When writing specifications, cite the applicable edition and require third party documentation consistent with the jurisdiction’s plumbing code adoption.
ASME standards reference page:
- ASME Plumbing Supply Fittings Reference Page
Water efficiency targets: flow and cycle limits
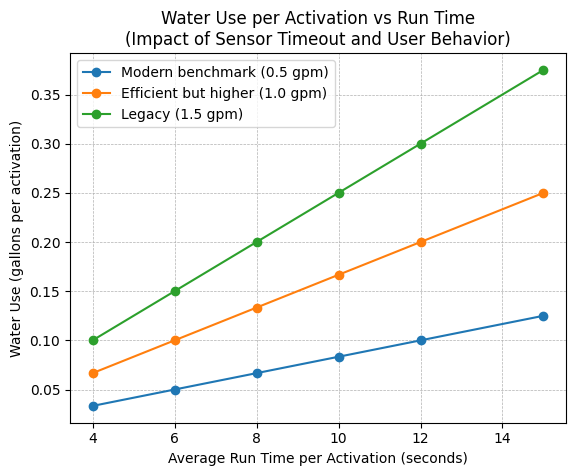
Public restroom water performance is commonly governed by a mix of federal requirements, state codes, and voluntary programs. For touchless and metering type fixtures, two practical checkpoints appear repeatedly in guidance:
- Public use lavatory faucets often align with 0.5 gpm maximum at 60 psi in many code pathways
- Metering faucets are often limited by a per cycle maximum in federal guidance
EPA WaterSense at Work guidance on commercial faucets provides useful framing for public versus private use contexts and references metering limits.
- WaterSense at Work Section 3.3 Faucets (PDF)
EPA WaterSense program product specifications overview:
- EPA WaterSense Product Specifications
For California projects or projects adopting CALGreen like performance targets, confirm whether the restroom is classified under public use and which tier applies. CALGreen references are typically handled at the code level rather than the fixture marketing level. The ICC hosted CALGreen code chapters are a practical reference during design coordination.
- CALGreen 2022 Chapter 5 Nonresidential Mandatory Measures
A consolidated summary table commonly used for CALGreen water requirements lists public bathroom faucet targets such as 0.5 gpm at 60 psi, which can help teams validate schedules against prescriptive requirements.
- 2022 CALGreen Water Requirements (PDF)
Durability Engineering: Materials, Hydraulics, and Serviceability
Materials and finish in real cleaning environments
In institutional restrooms, chemical compatibility matters as much as corrosion resistance. Many failures attributed to “finish quality” are really cleaning protocol issues: high concentration disinfectants, chlorine based products, and abrasive pads can damage coatings and seals. From a spec standpoint, the goal is to select products with durable base materials and finishes suitable for the owner’s maintenance practices, and then document approved cleaning methods in O and M.
Filtration, strainers, and debris tolerance
Commercial plumbing systems carry debris during commissioning, valve replacements, and periodic maintenance. Touchless faucets add solenoids and small orifices that are sensitive to particulates. Require either integrated strainers or upstream point filtration where appropriate. Also specify that strainers be accessible without removing the faucet body from the deck or wall.
Vandal resistance and tamper control
For airports, schools, and publicly accessible corporate campuses, vandal resistance is not a product feature. It is a maintenance cost control strategy. Look for:
- Aerators that resist removal or use keyed tools
- Fasteners and battery compartments that are not exposed
- Time out functions to prevent continuous flow in fault states
- Clear service access paths for staff
FontanaShowers product pages commonly list operational features such as sensor timeouts, low battery indication, and durability related notes, which should be verified against the project’s basis of design and the facilities team’s preferred service model.
- Fontana Antique Commercial Automatic Sensor
Power Architecture and Controls Integration
Battery versus hardwired power planning
Battery powered touchless faucets reduce rough in complexity but shift labor to periodic replacement and require access planning. Hardwired or AC fed options can reduce downtime and support standardized maintenance, but they require coordination for power routing, GFCI strategy, and access to transformers or power modules.
For AEC teams, treat power selection like any other system choice:
- Define replacement intervals and storage policy if battery powered
- Confirm access method for replacement without disrupting adjacent fixtures
- If hardwired, coordinate pathways, transformer locations, and service disconnect requirements
FontanaShowers commercial restroom listings note AC and DC power options on certain commercial electronic faucets, which is relevant for standardization across a portfolio.
- Touchless Restroom
Data and monitoring: where “integration” is realistic
Some owners request BMS integration for restroom usage, leak events, or fixture health. In practice, integration readiness depends on whether the faucet system provides discrete outputs, a gateway, or a compatible monitoring platform. If monitoring is part of the owner project requirements, define it explicitly in Division 25 or Division 23 sequences and do not assume fixture level connectivity.
A pragmatic approach is to specify:
- Simple fault indication at the fixture level for maintenance staff
- Isolation valves and access panels sized for rapid repair
- Standardized parts strategy across floors and buildings
Specification Language That Reduces Risk
Submittals and closeout documentation
For commercial touchless faucets, require:
- Manufacturer cut sheet with flow rate or cycle volume and power requirements
- Installation instructions with rough in dimensions
- Maintenance instructions including strainer cleaning procedure
- Warranty terms aligned with the project’s asset policy
When product pages include specification and installation documentation, link them in the submittal checklist so contractors and commissioning teams use the correct revision set.
- Commercial Bathroom Matte Black Automatic Touchles
Commissioning checks that catch problems early
Add fixture level checks to the commissioning plan:
- Verify sensor range and false activation behavior in final lighting conditions
- Confirm flow rate at representative pressure conditions
- Validate hot limit and tempered water temperatures where applicable
- Record battery install dates or transformer locations for O and M
Closing Notes for AEC Teams
FontanaShowers’ commercial touchless faucet line can be evaluated the same way you would evaluate any high use plumbing component: by documentation quality, maintainability, standards alignment, and measurable water performance. The most effective specifications connect the faucet selection to upstream filtration, mixing strategy, accessibility coordination, and an owner defined maintenance plan. That is what turns a “touchless faucet” into a reliable restroom system component rather than a recurring service ticket.
Standards and guidance references used above
| Category | Specification focus (AEC) | Typical requirement or design target | Reference (live link, no tracking) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Coordinate sensor activation, spout reach, and mounting height with lavatory geometry and clearances. Ensure operation does not require grasping, pinching, or twisting. | 2010 ADA Standards (installation dependent). |
2010 ADA Standards (Landing Page)
Open
|
| Accessibility | Use the official technical criteria during layout and compliance review sets. | 2010 ADA Standards PDF. |
ADA Standards (PDF)
Open
|
| Water efficiency | Set public lavatory faucet flow limits in fixture schedules and verify at design pressure where applicable. Require rated flow documentation in submittals. | Public use lavatory benchmark often aligns at 0.5 gpm (program and code dependent). |
WaterSense at Work Section 3.3 Faucets (PDF)
Open
|
| Water efficiency programs | If WaterSense is required, define the compliance pathway and submittal documentation expectations. | WaterSense product specification framework (category specific). |
EPA WaterSense Product Specifications
Open
|
| CALGreen coordination | Confirm the adopted CALGreen edition and map public versus private restroom classification to prescriptive requirements. | Nonresidential mandatory measures (edition dependent). |
CALGreen 2022 Chapter 5 Nonresidential Mandatory Measures
Open
|
| CALGreen quick check | Use as a quick validation against fixture schedules, then confirm against locally adopted code requirements. | Often lists 0.5 gpm at 60 psi for public bathroom faucets (verify locally). |
2022 CALGreen Water Requirements (PDF)
Open
|
| Performance standards | Require compliance with recognized plumbing supply fitting performance standards and match editions to AHJ and code adoption. | ASME plumbing supply fittings reference. |
ASME Plumbing Supply Fittings Reference Page
Open
|
| FontanaShowers commercial categories | Use category pages to shortlist basis of design options, then confirm power, flow, and service access per model. | Touchless restroom category hub. |
Touchless Restroom
Open
|
| FontanaShowers commercial categories | Cross check commercial models across touchless faucet listings and verify installation constraints. | Touchless faucet category hub. |
Touchless Faucet
Open
|
| FontanaShowers product example | Use the product detail page format as a reference for submittal attributes such as flow, power type, and installation notes. | Example commercial touchless faucet PDP. |
Commercial Bathroom Matte Black Automatic Touchles
Open
|
| Graph assumptions | Use only for early stage water modeling. Replace with measured usage and owner standards during DD and CD. | 10 second average run time per activation. Traffic scenarios 250 to 2000 activations per day. Flow rates 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 gpm. | N/A (derived from the article discussion) |
